Pagejacking
Pagejacking is the process of illegally copying legitimate website content (usually, in the form of source code) to another website designed to replicate the original website. A pagejacker's intention is to illegally direct traffic from the original site to cloned Web pages. Pagejackers rely on search engines to index bogus site content to enable search result ranking and display with the original site.
Pass-Along Rate
A pass-along rate represents the percentage of people who pass on a message or file. Indeed, pass-along rates are a measure of word-of-mouth marketing. Objects typically passed include email messages, Web pages and multimedia files. Content typically passed includes humor and entertainment, late-breaking news, shopping specials, and technical gizmos.
Passive Authentication
In a passive authentication scenario a user is directed to a login page, and after logging in, the site directs the user back to the URL and allow the user to be authenticated on that site. The passive authentication can be achieved by using WS-Federation protocol or SAML 2.0.
Payables Fraud
Payable fraud, also known as AP fraud, is among the most ubiquitous and damaging of frauds that affect businesses of all sizes. It's also among the easiest frauds to perpetrate, since most of the money leaving a company legitimately goes through the accounts payable function.
Paying Personal Expenses
Paying personal expenses refers to the expenses of an individual that are not related to business or investment purposes. Personal expenses are not deductible unless specifically allowed under the tax law. Two examples of deductible personal expenses are medical expenses and personal property tax paid on personal-use property. Deductible expenses are returned when an employee creates and sends an invoice to the company, and in return the company will give them the money to pay those personal expenses.
Payment Application Data Security Standard
Payment Application Data Security Standard (PA-DSS) is a set of requirements that are intended to help software vendors to develop secure payment applications that support PCI DSS compliance.
Payment Fraud
Payment fraud is a blanket term for a variety of different frauds that all center around using false information or unauthorized means to make a purchase. This type of fraud can roughly be categorized into three kinds of situations; relating to fraudulent or illegal transactions, misplaced or stolen goods, and false requests for reimbursements or returns on goods.
Payment Gateway
A Payment Gateway processes credit card and debit card payments, as well as other forms of electronic payments, primarily on behalf of e-commerce and brick-and-mortar merchants. The Payment Gateway is responsible for authenticating, standardizing and relaying transaction data between the merchants and the payment processors. The payment gateway responsibilities include securing payment data according to PCI DSS standards, securely sending transaction data to the payment processor, and storing the transaction and subsequent settlement, refund and other financial event data for later access by the merchant. Banks often own the payment gateways, but payment service providers (PSPs) like PayPal, Square or Stripe can also create their own Payment Gateway software.
Payment Threshold
A payment threshold defines a situation in online marketing where an associate has to meet a certain criteria, generally a number of sales, before being paid by the affiliate company for their services.
Payment Verification
What is Payment Verification?
Payment verification is a crucial process that helps safeguard financial transactions from fraudulent activities. It involves the thorough examination and validation of payment information provided by users before authorizing a transaction. By confirming the legitimacy of payments, businesses can mitigate the risk of fraud, chargebacks, and unauthorized transactions, thereby ensuring a safe and trustworthy environment for both customers and merchants.
Here are some statistics about payment fraud: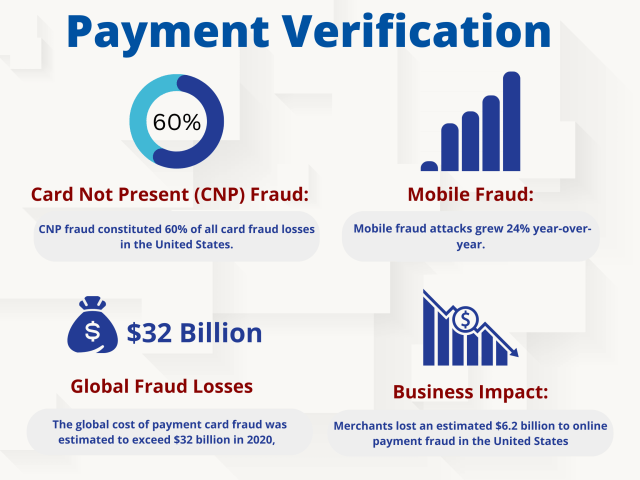
- The 2023 AFP Payments Fraud and Control Survey reports that 65% of organizations were victims of payment fraud attacks/attempts in 2022.
- Payment fraud losses are projected to hit $49 billion by 2030, and payment fraud is expected to continue increasing.
- The global cost of online payment fraud is expected to reach $206 billion by 2025, up from $130 billion in 2020.
These statistics highlight the importance of payment verification in preventing fraud and protecting businesses and consumers from financial losses.
Common Types of Verification
Address Verification System (AVS): AVS cross-references the billing address provided during a transaction with the address on file with the card-issuing bank. Any discrepancies could raise a red flag for potential fraud.
Card Verification Value (CVV): The CVV is a three or four-digit code found on the back of credit and debit cards. It adds an extra layer of security as it is not stored in the magnetic stripe or chip and must be entered during online transactions.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): This method requires users to provide a secondary piece of information, such as a one-time code sent to their mobile device, in addition to their payment credentials.
How Does Payment Verification Differ from Payment Authentication?
While verification focuses on confirming the accuracy of the provided payment details, authorization is the step that seeks approval from the issuing bank to complete the transaction. Payment authentication, on the other hand, is a broader term that encompasses various methods, including verification, designed to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the security of transactions.
Solutions for Payment Verification – AI Fraud Prevention with Verification
In today’s technologically advanced landscape, fraudsters continually adapt their tactics to exploit vulnerabilities. Traditional methods of payment verification may not be sufficient to combat the growing threat of fraud. As such, businesses are turning to AI-powered fraud prevention tools that integrate robust payment verification processes.
AI-driven solutions offer real-time analysis of payment data and user behavior, identifying suspicious patterns and swiftly detecting potential fraud attempts. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these tools evolve and adapt to new threats, providing dynamic and reliable protection against ever-changing fraud schemes.
Fraud.net’s Solution
At Fraud.net, we recognize the criticality of safeguarding your business and customers against fraud. Our AI-powered fraud prevention platform seamlessly incorporates advanced payment verification capabilities to ensure the integrity of every transaction. With real-time analysis and comprehensive risk assessment, our solution empowers businesses to identify and prevent fraudulent activities before they cause harm.
Discover how Fraud.net’s Transaction AI solution can fortify your business against fraud threats. Book a demo today to explore the powerful features of our AI-driven platform and experience the peace of mind that comes with enhanced security. Safeguard your transactions and reputation with Fraud.net – your trusted partner in fraud prevention.
PayPal
PayPal Holdings, Inc. is an American company that operates a universal online payment method that supports online money transfers. It also serves as an electrical substitute for the usual paper-based methods of checks and money orders. The company functions as a payment mainframe for online vendors, auction sites, and numerous other business users. These users are usually charged an interbank fee for profits such as one-click transactions and password memory.
History of PayPal
The Beginning
PayPal, first founded as Confinity, resulted from a collaboration between Max Levchin, Peter Thiel, and Luke Nosek. They developed it as a digital wallet solution, a way to send payments through email, releasing its first iteration in 1999.
In 2000, Confinity merged with X.com, an online banking service founded by Elon Musk. Peter Thiel then replaced Elon Musk as CEO in October 2000, and renamed Confinity to PayPal Holdings in 2001. They went public in 2002, at $13 per share, minting over $61 million.
Acquired by eBay
Within the same year, they were acquired by eBay, and the service supported 70% of auctions and transactions. Accordingly, it became the default payment method for online transactions on eBay.
Versus Anonymous
In July 2011, Anonymous was charged with attempting to disrupt PayPal operations. They attempted denial of service attacks in December of the previous year. These attacks were an act of retaliation against the company's denial to process donation transactions to WikiLeaks.
eBay and PayPal Part Ways
eBay and PayPal split into two separate companies in 2015, but their professional partnership remained alive. The latter continues to offer a payment option for eBay shoppers, but not as a transaction processing platform.
Social Media Ventures
Instagram and PayPal partnered in 2019 for Instragam shopping, offering "Checkout on Instagram" with the latter as part of the feature. In 2020 they acquired Honey, a browser extension that scrubs for the largest discounts available at various shopping locations.
Why is it so Popular?
PayPal operates in 202 global markets and has 377 million active accounts. It grew to this popularity due to the ease of use they offered for transactions.
Users could transfer money without credit cards or paper options and could do so between different banking institutions and credit unions. This was especially helpful in cases where people could not obtain credit cards due to their financial history. In these cases, it acted as a prepaid "card", in which one could transfer money from their debit card to create a "balance" to then use to pay for transactions.
It also offered automatic currency conversion options for those making international transactions. Due to their investments in transaction security and providing a variety of options and personalizations for users, PayPal has sustained itself as a major payment platform.
What Does PayPal have to do with Fraud?
While PayPal has invested in securing its platform over the years, the platform is still vulnerable to fraudulent activity and has a history of combatting it.
2001
International hackers targeted PayPal accounts, transferring small amounts of money out of multiple accounts. In response, they developed an AI-powered fraud detection system to detect potentially fraudulent transactions. Peter Thiel, inspired by this development, went on to create Palantir.
2015
In this instance, a PayPal service provider charged 150,000 Spanish cardholders an unauthorized €15. Most funds were returned.
Retaliation for Banning Transactions
As stated earlier, PayPal fell victim to a denial of service attack by hacktivist group Anonymous, in retaliation against their banning of donations to WikiLeaks. They may continue to face these types of attacks due to their controversial banning of several transactions and accounts associated with human rights activism or non-traditional work.
Additionally, PayPal's service acting as a "prepaid" card of sorts provides an opportunity for scammers to facilitate money laundering through their service. PayPal does comply with AML standards set forth by government cybersecurity jurisdictions, but the service still faces audits for failed compliance and deals with laundering today.
Fraud.net's Protection and Detection Solutions
Fraud.net offers a wide variety of products and solutions to combat money laundering, business email compromise, and invoice fraud. Contact us for a free demo today, and product recommendations and best practices for your business.
Paypal Fraud
What is PayPal Fraud?
PayPal fraud is fraud related to using the paypal payment system. It can be initiated or performed through emails, phishing sites, malevolent ads, doubtful links, and many more. These scams try to appear authentic in order to trick users into releasing personal information, such as usernames and passwords, or to illegally obtain payments and payment info.
A fake paypal invoice or email may look like the consumer has to take an action by clicking on any fraudulent links. If you review an item purchased that was not made by you on your account, report a problem, select the transaction, hit dispute and click continue. It’s extremely important to report any suspected instances of Paypal fraud immediately after you view your transactions to protect your account and information.
How to Protect Against PayPal Fraud
The most effective protection against PayPal fraud is education on what to look out for. Phishing emails can usually be spotted under close scrutiny. There are tells like misspellings or a “re:” at the beginning of the subject line.
If you receive an email or notification that you owe money or there’s been a mistake with your account, it’s almost definitely a phishing attempt. To double check, log into your account through the PayPal website rather than through any links present on the notification.
Fraudsters will sometimes also try to tempt their victims with offers of payment that sound too good to be true. Sounding too good to be true is a major indication that it isn’t true.
Fraud.net Solutions
Fraud.net offers a variety of solutions using AI and machine learning to prevent fraud attacks of all kinds and therefore, your bottom line. We offer dark web monitoring, analytics and reporting, identity protection services, and more.
Contact us for a demo and recommendations for fraud prevention and identity verification.
Payroll Fraud
Payroll Fraud is a category of accounting fraud typically carried out by people who have access to employee information, their incomes or their wages. Companies that have not applied the accurate controls in their financial section – particularly in times of financial distress – will face more complex fraud risks than other companies.


